Imagine a dinosaur that roamed the Earth millions of years ago, sporting an astonishing dinosaur has 500 teeth. Yes, you read that right! Meet the Nigersaurus, a remarkable creature from the Late Jurassic period that has captured the fascination of paleontologists and dinosaur enthusiasts alike. With its unique dental structure and distinct physical traits, this herbivorous giant offers insights into prehistoric life like no other. Dive in as we uncover everything there is to know about this extraordinary dinosaur with an impressive toothy smile!
Discovery and Naming of the Dinosaur
The Nigersaurus dinosaur was first discovered in the 1970s in Niger, a country rich in prehistoric fossils. Paleontologists unearthed its remains during an expedition that aimed to explore the diversity of dinosaurs in Africa. Named by Dr. Paul Sereno and his team, “Nigersaurus” translates to “Niger lizard.” The name reflects both its geographical origin and its reptilian nature.
Fossils revealed key features, sparking interest among scientists. They noted its unique dental structure early on. This sparked debates about Nigersaurus’s diet and lifestyle compared to other herbivorous dinosaurs. As more findings emerged over the years, researchers continued to refine their understanding of this fascinating creature. Each new fossil added another layer to the story of one remarkable dinosaur with an astonishing number of teeth—500, to be exact!
Physical Characteristics and Behavior
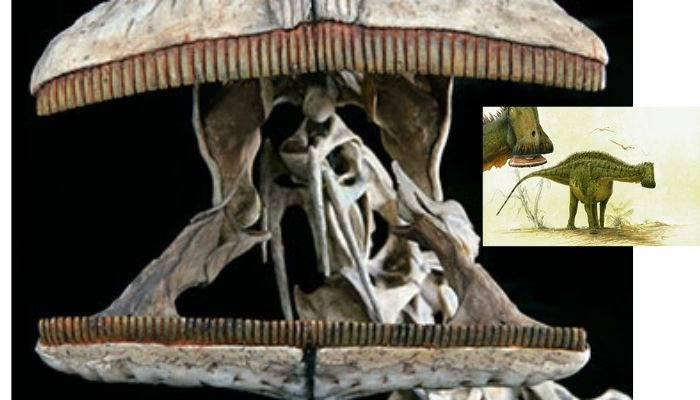
Nigersaurus was a fascinating creature from the Late Jurassic period. It stood out with its long neck and relatively lightweight body, making it an agile herbivore. Measuring around 30 feet in length, this dinosaur had a unique silhouette. Its most striking feature was its broad, shovel-shaped skull. The head housed an impressive array of approximately 500 teeth, perfectly adapted for grazing on low-lying vegetation.

Unique Dental Structure of Nigersaurus
The Nigersaurus boasts a truly unique dental structure that sets it apart from other dinosaurs. With around 500 teeth, this herbivore was designed for a specialized diet. Its teeth were not just numerous; they had an intriguing shape. These teeth were flat and adapted to grazing on low-lying vegetation. Unlike the pointed teeth of carnivorous dinosaurs, Nigersaurus’ dental arrangement allowed it to efficiently shear through soft plants. This adaptation made it well-suited for its environment during the Late Jurassic period.
What makes this dinosaur even more fascinating is how its jaw worked in unison with its extensive tooth count. The jaw could move side to side, allowing Nigersaurus to maximize contact with food as it fed close to the ground. This innovative dental system reflects evolutionary ingenuity and reveals much about the feeding strategies of ancient herbivores.
Diet and Feeding Habits of Nigersaurus
The Nigersaurus had a fascinating diet that set it apart from other dinosaurs. This herbivorous giant primarily fed on low-lying plants, grasses, and leaves found in its lush environment. Its unique teeth played a crucial role. With around 500 specialized teeth, they were perfect for grazing. The dinosaur would often use its wide mouth to sweep across the ground, efficiently gathering vegetation. Nigersaurus likely employed a browsing technique similar to modern-day giraffes and elephants. It could reach various types of foliage without needing to chew extensively. This feeding behavior allowed it to thrive in diverse habitats.
Additionally, some scientists believe that Nigersaurus may have occasionally used its teeth for social interactions or displays within its species. Understanding these dietary habits helps paint a vivid picture of life during the time of this remarkable dinosaur.
Extinction and Fossil Findings of Nigersaurus
Nigersaurus, a fascinating dinosaur from the Late Jurassic period, met its demise millions of years ago. Its extinction is still shrouded in mystery, but several theories exist. Changing climates and shifting vegetation could have played significant roles. Fossil findings provide vital clues about this unique creature. Discovered in Niger’s Sahara Desert during the 1970s, Nigersaurus remains have been unearthed in remarkable quantities. Paleontologists identified numerous vertebrae and skull fragments.
What makes these fossils particularly intriguing is their exceptional preservation condition. They offer insights into the dinosaur’s life and environment. The large number of teeth found alongside other skeletal parts suggests specialized feeding habits that influenced Nigersaurus’ role in its ecosystem. These discoveries not only reveal information on Nigersaurus itself but also contribute to our understanding of prehistoric life during its era.
Impact on Scientific Understanding of Nigersaurus Dinosaur
The discovery of Nigersaurus has significantly reshaped paleontological perspectives. This dinosaur’s unique dental structure challenged existing theories about herbivorous dinosaurs and their feeding methods. Researchers previously assumed that a few large teeth were sufficient for processing vegetation. Nigersaurus, with its 500 closely packed teeth, suggested a different approach to herbivory – one focused on grazing rather than browsing.
This new insight into the dietary habits of dinosaurs led scientists to explore adaptive strategies across various species during the Late Jurassic period. It opened avenues for understanding how these creatures interacted with their environment. Moreover, Nigersaurus has sparked discussions around the biomechanical advantages of having so many teeth in terms of efficiency in feeding. Its specialized adaptation provided clues about ecosystem dynamics long before humans roamed the Earth.
Modern Day Examples of Animals with Similar Dental Adaptations
In the animal kingdom, there are fascinating creatures that echo the unique dental adaptations of Nigersaurus. Take the manatee, for instance. These gentle giants continuously grow new teeth throughout their lives, much like Nigersaurus’ ever-replenishing dental set. Another example is the modern-day iguana. With its sharp, peg-like teeth designed for stripping leaves and vegetation, it showcases a similar feeding strategy to that of our dinosaur friend.
Then there’s the duiker—a small African antelope with specialized molars perfect for grinding down tough plant material. Their dentition allows them to thrive in dense bush habitats where foliage is abundant. These animals illustrate how effective evolutionary strategies have persisted over time. Just as Nigersaurus adapted to its environment millions of years ago, these contemporary species continue to showcase remarkable tooth adaptations tailored for survival.
Conclusion
The Nigersaurus stands out as a fascinating example of dinosaur diversity. With its unique dental structure, it challenged previous notions about feeding mechanisms in herbivorous dinosaurs. This creature not only had an impressive 500 teeth but also showcased adaptations that allowed it to thrive in its environment. Through the study of Nigersaurus fossils, scientists have gained insights into the ecosystems of the Cretaceous period. The findings continue to inspire researchers and spark curiosity among enthusiasts alike.
Modern-day animals with similar dental adaptations remind us that nature often finds inventive solutions for survival. Just like the Nigersaurus, these creatures exhibit how evolution shapes biology over millions of years. As we explore more about this intriguing dinosaur, we deepen our understanding of prehistoric life and appreciate the remarkable variety once present on Earth. The legacy of Nigersaurus continues to enrich our knowledge and ignite imagination in paleontology circles around the globe.